Ever pause to think about the sheer volume of electricity that powers our modern world? From the devices in our pockets to the factories churning out goods, it all runs on watts and volts. Now, imagine a single nation generating more electricity than two of the world’s largest economic blocs combined. Sounds like a sci-fi plot, doesn’t it? Yet, this isn’t fiction. China has quietly, and with incredible speed, ascended to an unprecedented position in global electricity generation, now producing a staggering 40% more power than the United States and the European Union combined. This isn’t just a statistic; it’s a seismic shift reshaping global economics, industry, and even our environmental future.
Defining the Gigawatt Gap: What These Numbers Really Mean
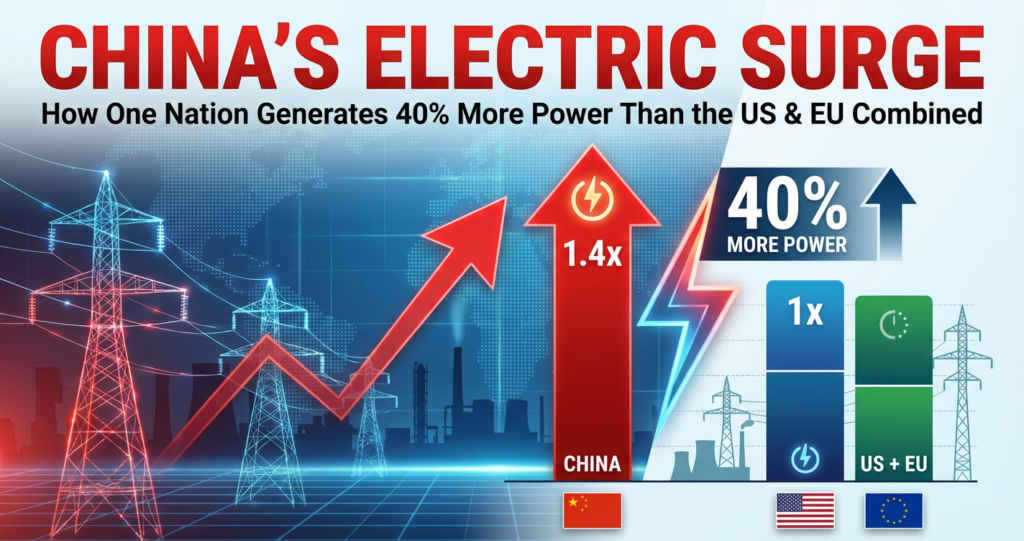
When we talk about “electricity generation,” we’re measuring the total amount of electrical energy produced over a period, typically in tera watt-hours (TWh). Think of it as the ultimate power output of a nation’s entire energy infrastructure. The data, particularly from sources like Our World in Data, paints a vivid picture:
- A Dramatic Ascent: For decades, the US and Europe were global leaders in electricity output, reflecting their mature industrial economies. China, while growing, was a distant third.
- The Crossover: Sometime around the early 2010s, China’s generation curve began its sharp, almost vertical climb, surpassing the US, then the EU, and eventually, their combined total.
- The Current Reality (as of 2024/2025): China’s output is now well over 10,000 TWh annually, while the US hovers around 4,300 TWh and the EU around 2,700 TWh. Add those two together, and you get approximately 7,000 TWh. The 40% difference isn’t an exaggeration; it’s a conservative estimate of a truly monumental gap.
This isn’t just about big numbers; it’s about the underlying capacity and the raw energy flowing through the veins of a nation.
The Power Behind the Dragon: Why This Is Happening
So, how did this happen, and why China? Several interconnected factors fuel this unprecedented surge:
- The World’s Factory Floor: This is perhaps the most significant driver. China has firmly established itself as the global manufacturing hub. From electronics to textiles, heavy machinery to solar panels, countless goods consumed worldwide are produced in Chinese factories. Each factory, each production line, demands immense amounts of electricity.
- Rapid Urbanization and Infrastructure Development: China has undergone an unparalleled transformation, with hundreds of millions moving from rural areas to burgeoning cities. This requires building colossal urban centers, extensive transportation networks (like high-speed rail), and modern infrastructure—all of which are massive energy consumers.
- Electrification of Everything: While Western nations are actively decarbonizing their grids, China is simultaneously electrifying its economy at a rapid pace. This includes the massive adoption of electric vehicles (China is the world leader in EV sales and production), electric heating, and other applications that shift energy demand directly onto the grid.
- Massive Energy Investments (Both Fossil & Renewable): It’s crucial to understand that China’s energy expansion isn’t a one-trick pony. They are simultaneously the world’s largest builder of new coal-fired power plants and the world leader in renewable energy installations, particularly solar and wind. This dual-track approach ensures an ever-growing supply to meet insatiable demand.
Navigating the Current: Implications and Global Guidelines
This dramatic shift has profound implications that ripple across the globe:
- Economic Clout: Such immense power generation capability underpins China’s economic strength and its ability to produce goods at scale and competitive prices.
- Geopolitical Influence: Energy independence (or at least, massive internal production) is a significant geopolitical asset.
- Environmental Dilemmas: While China is rapidly investing in renewables, the sheer scale of its energy demand means that fossil fuels still constitute a significant portion of its energy mix, posing challenges for global climate goals. However, the renewable build-out is equally unprecedented.
- Technological Advancement: This scale of energy production requires constant innovation in grid management, smart technologies, and ultra-high-voltage transmission.
For other nations, the “rules” or “guidelines” from observing China’s journey might include:
- Strategic Energy Planning: Having a long-term, comprehensive energy strategy is paramount.
- Diversification is Key: Relying on a single energy source is risky; a mix of traditional and renewable sources provides resilience.
- Infrastructure Investment: Modernizing and expanding energy infrastructure is critical for economic growth and stability.
- Embrace Electrification: As economies evolve, the shift towards electric power in transport and industry is inevitable and requires proactive planning.
FAQs: Your Questions About China’s Power Answered
Q: Does this mean China is more environmentally friendly? A: Not necessarily. While China is a massive investor in renewables (solar, wind, hydro), the sheer scale of its energy demand still necessitates significant reliance on coal. Its total emissions remain very high, though it’s also installing more clean energy than any other nation.
Q: Is this sustainable in the long run? A: China’s dual strategy of expanding both fossil fuels and renewables suggests it’s prioritizing energy security and economic growth above all else. The long-term sustainability hinges on how quickly it can pivot to a predominantly renewable grid.
Q: How does this impact global supply chains? A: China’s abundant and relatively cheap electricity is a core reason why so much manufacturing has congregated there. Any instability in its energy supply could have significant ripple effects on global production and prices.
Q: Are the US and EU falling behind? A: “Falling behind” isn’t quite the right term. The US and EU have more mature economies and are often focused on transitioning to cleaner, more efficient energy systems, sometimes with less overall growth in demand. China is in a different stage of development, with massive expansion still underway.
Conclusion: A New Era of Global Power
The story of China’s electricity generation isn’t just about impressive charts and statistics; it’s a powerful narrative of ambition, industrialization, and rapid development that has fundamentally reshaped the global energy landscape. The fact that one nation now generates 40% more electricity than the combined might of the US and EU is a stark reminder of shifting economic gravity and the immense scale of China’s industrial engine.
This era of unparalleled power production presents both opportunities and challenges, from powering global consumption to addressing environmental concerns. Understanding this colossal shift isn’t just for economists or energy experts—it’s crucial for anyone seeking to comprehend the forces shaping our world today and tomorrow.
What do you think about this incredible energy shift? Share your thoughts in the comments below!